Tutorial 9: Camera on the Home Network
This document will provide a walk-through tutorial to use the Open GoPro Interface to configure and demonstrate the Camera on the Home Network (COHN) feature.
Requirements
It is assumed that the hardware and software requirements from the connecting BLE tutorial are present and configured correctly.
The scripts that will be used for this tutorial can be found in the Tutorial 9 Folder.
Just Show me the Demo(s)!!
-
Each of the scripts for this tutorial can be found in the Tutorial 9 directory.
Python >= 3.9 and < 3.12 must be used as specified in the requirementsYou can provision the GoPro for COHN to communicate via a network via:
$ python provision_cohn.pySee the help for parameter definitions:
$ python provision_cohn.py --help usage: provision_cohn.py [-h] [-i IDENTIFIER] [-c CERTIFICATE] ssid password Provision COHN via BLE to be ready for communication. positional arguments: ssid SSID of network to connect to password Password of network to connect to options: -h, --help show this help message and exit -i IDENTIFIER, --identifier IDENTIFIER Last 4 digits of GoPro serial number, which is the last 4 digits of the default camera SSID. If not used, first discovered GoPro will be connected to -c CERTIFICATE, --certificate CERTIFICATE Path to write retrieved COHN certificate.You can see an example of communicating HTTPS via COHN (assuming it has already been provisioned) via:
$ python communicate_via_cohn.pySee the help for parameter definitions:
$ python communicate_via_cohn.py --help usage: communicate_via_cohn.py [-h] ip_address username password certificate Demonstrate HTTPS communication via COHN. positional arguments: ip_address IP Address of camera on the home network username COHN username password COHN password certificate Path to read COHN cert from. options: -h, --help show this help message and exit -
TODO
Setup
We must first connect to BLE as was discussed in the
connecting BLE tutorial.
The GoPro must then be connected to an access point as was discussed in the
Connecting WiFi Tutorial.
For all of the BLE operations, we are using the same ResponseManager class that was defined in the
Protobuf tutorial.
COHN Overview
The Camera on the Home Network feature allows the GoPro to connect (in Station Mode) to an Access Point (AP) such as a router in order to be controlled over a local network via the HTTP API.
In order to protect users who connect to a network that includes Bad Actors, COHN uses
SSL/TLS so that command and responses are
sent securely encrypted via https:// rather than http://.
Provisioning
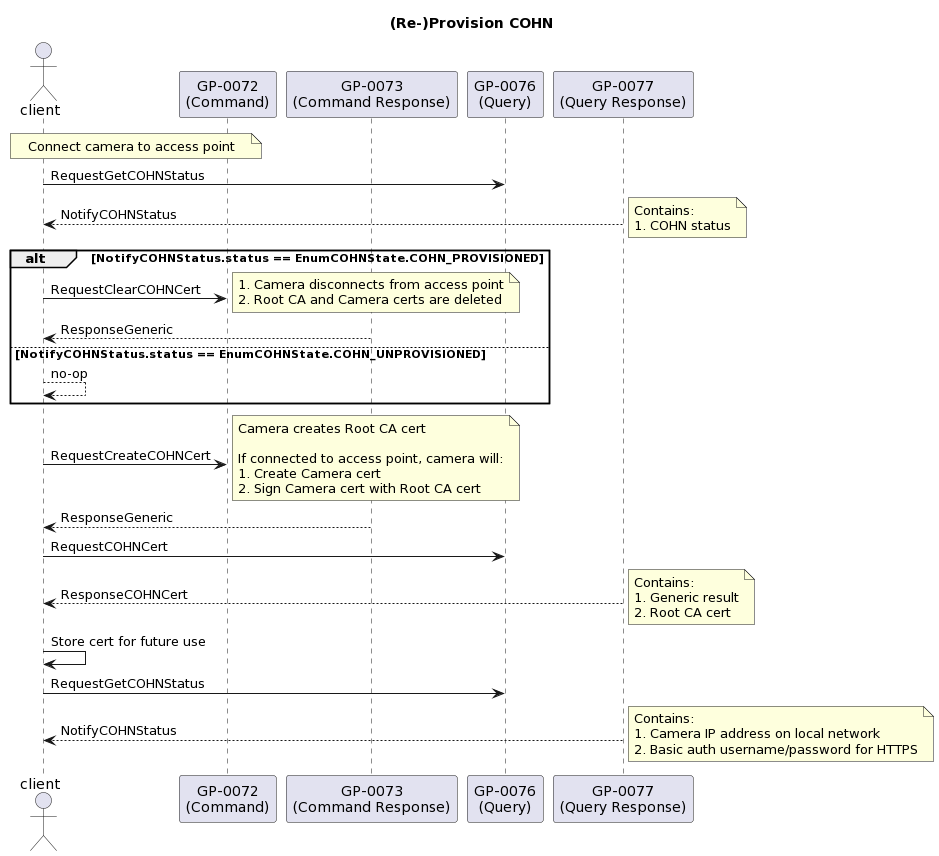
In order to use the COHN capability, the GoPro must first be provisioned for COHN via BLE. At a high level, the provisioning process is as follows:
- Connect the GoPro to an access point
- Instruct the GoPro to create a COHN Certificate
- Get the created COHN certificate
- Get the COHN status to retrieve and store COHN credentials for future use
A summary of this process is shown here and will be expanded upon in the following sections:
Set Date Time
While not explicitly part of of the provisioning process, it is important that the GoPro’s date and time are correct so that it generates a valid SSL certificate. This can be done manually through the camera UI or programatically using the Set Local Datetime command.
For the provisioning demo discussed in this tutorial, this is done programatically:
-
The code shown here can be found in
provision_cohn.pyWe’re using the pytz and tzlocal libraries to find the timezone offset and daylight savings time status. In the
set_date_timemethod, we send the request and wait to receive the successful response:datetime_request = bytearray( [ 0x0F, # Command ID 10, # Length of following datetime parameter *now.year.to_bytes(2, "big", signed=False), # uint16 year now.month, now.day, now.hour, now.minute, now.second, *offset.to_bytes(2, "big", signed=True), # int16 offset in minutes is_dst, ] ) datetime_request.insert(0, len(datetime_request)) await manager.client.write_gatt_char(GoProUuid.COMMAND_REQ_UUID.value, datetime_request, response=True) response = await manager.get_next_response_as_tlv()which logs as:
Setting the camera's date and time to 2024-04-04 13:00:05.097305-07:00:-420 is_dst=True Writing: 0c:0f:0a:07:e8:04:04:0d:00:05:fe:5c:01 Received response at GoProUuid.COMMAND_RSP_UUID: 02:0f:00 Successfully set the date time. -
TODO
Create the COHN Certificate
Now that the GoPro’s date and time are valid and it has been connected to an Access Point, we can continue to provision COHN.
Let’s instruct the GoPro to Create a COHN certificate.
-
create_request = bytearray( [ 0xF1, # Feature ID 0x67, # Action ID *proto.RequestCreateCOHNCert().SerializePartialToString(), ] ) create_request.insert(0, len(create_request)) await manager.client.write_gatt_char(GoProUuid.COMMAND_REQ_UUID.value, create_request, response=True) response := await manager.get_next_response_as_protobuf()which logs as:
Creating a new COHN certificate. Writing: 02:f1:67 Received response at GoProUuid.COMMAND_RSP_UUID: 04:f1:e7:08:01 COHN certificate successfully created -
TODO
Get the COHN Credentials
At this point the GoPro has created the certificate and is in the process of provisioning COHN. We now need to get the COHN credentials that will be used for HTTPS communication. These are:
We can immediately get the COHN certificate as such:
-
cert_request = bytearray( [ 0xF5, # Feature ID 0x6E, # Action ID *proto.RequestCOHNCert().SerializePartialToString(), ] ) cert_request.insert(0, len(cert_request)) await manager.client.write_gatt_char(GoProUuid.QUERY_REQ_UUID.value, cert_request, response=True) response := await manager.get_next_response_as_protobuf(): cert_response: proto.ResponseCOHNCert = response.data # type: ignore return cert_response.cert -
TODO
For the remaining credentials, we need to wait until the COHN network is connected. That is, we need to Get COHN Status until we receive a status where the state is set to COHN_STATE_NetworkConnected. This final status contains the remaining credentials: username, password, and IP Address.
To do this, we first register to receive asynchronous COHN status updates:
-
status_request = bytearray( [ 0xF5, # Feature ID 0x6F, # Action ID *proto.RequestGetCOHNStatus(register_cohn_status=True).SerializePartialToString(), ] ) status_request.insert(0, len(status_request)) await manager.client.write_gatt_char(GoProUuid.QUERY_REQ_UUID.value, status_request, response=True) -
TODO
Then we continuously receive and check the updates until we receive the desired status:
-
while response := await manager.get_next_response_as_protobuf(): cohn_status: proto.NotifyCOHNStatus = response.data # type: ignore if cohn_status.state == proto.EnumCOHNNetworkState.COHN_STATE_NetworkConnected: return cohn_statusThis will all display in the log as such:
Checking COHN status until provisioning is complete Writing: 04:f5:6f:08:01 ... Received response at GoProUuid.QUERY_RSP_UUID: 20:47:f5:ef:08:01:10:1b:1a:05:67:6f:70:72:6f:22:0c:47:7a:74 Received response at GoProUuid.QUERY_RSP_UUID: 80:32:6d:36:59:4d:76:4c:41:6f:2a:0e:31:39:32:2e:31:36:38:2e Received response at GoProUuid.QUERY_RSP_UUID: 81:35:30:2e:31:30:33:30:01:3a:0a:64:61:62:75:67:64:61:62:75 Received response at GoProUuid.QUERY_RSP_UUID: 82:67:42:0c:32:34:37:34:66:37:66:36:36:31:30:34 Received COHN Status: status: COHN_PROVISIONED state: COHN_STATE_NetworkConnected username: "gopro" password: "Gzt2m6YMvLAo" ipaddress: "192.168.50.103" enabled: true ssid: "dabugdabug" macaddress: "2474f7f66104" Successfully provisioned COHN. -
TODO
Finally we accumulate all of the credentials and log them, also storing the certificate to a cohn.crt file:
-
credentials = await provision_cohn(manager) with open(certificate, "w") as fp: fp.write(credentials.certificate) logger.info(f"Certificate written to {certificate.resolve()}"){ "certificate": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\nMIIDnzCCAoegAwIBAgIUC7DGLtJJ61TzRY/mYQyhOegnz6cwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQ EL\nBQAwaTELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxCzAJBgNVBAgMAkNBMRIwEAYDVQQHDAlTYW4gTWF0\nZW8xDjAMBg NVBAoMBUdvUHJvMQ0wCwYDVQQLDARIZXJvMRowGAYDVQQDDBFHb1By\nbyBDYW1lcmEgUm9vdDAeFw0y NDA0MDQyMDAwMTJaFw0zNDA0MDIyMDAwMTJaMGkx\nCzAJBgNVBAYTAlVTMQswCQYDVQQIDAJDQTESMB AGA1UEBwwJU2FuIE1hdGVvMQ4w\nDAYDVQQKDAVHb1BybzENMAsGA1UECwwESGVybzEaMBgGA1UEAwwR R29Qcm8gQ2Ft\nZXJhIFJvb3QwggEiMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4IBDwAwggEKAoIBAQC05o1QIN5r\n PmtTntzpzBQvfq64OM1j/tjdNCJsyB9/ipPrPcKdItOy+5gZZF8iOFiw8cG8O2nA\nvLSIJkpQ6d3cuE 48nAQpc1+jJzskM7Vgqc/i43OqnB8iTKjtNJgj+lJtreQBNJw7\nf00a0GbbUJMo6DhaW58ZIsOJKu3i +w8w+LNEZECfDN6RMSmkYoLXaHeKAlvhlRYv\nxkNO7pB2OwhbD9awgzKVTiKvZ8Hrxl6lGlH5SHHimU uo2O1yiNKDWv+MhirCVnup\nVvP/N5S+230KpXreEnHmo65fsHmdM11qYu8WJXGzOViCnQi24wgCuoMx np9hAeKs\nVj4vxhyCu8gZAgMBAAGjPzA9MA8GA1UdEwQIMAYBAf8CAQAwCwYDVR0PBAQDAgGG\nMB0G A1UdDgQWBBTYDT4QXVDsi23ukLr2ohJk5+8+gDANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOC\nAQEAU4Z9120CGtRGo3 QfWEy66BGdqI6ohdudmb/3qag0viXag2FyWar18lRFiEWc\nZcsqw6i0CM6lKNVUluEsSBiGGVAbAHKu +fcpId5NLEI7G1XY5MFRHMIMi4PNKbJr\nVi0ks/biMy7u9++FOBgmCXGAdbMJBfe2gxEJNdyU6wjgGs 2o402/parrWN8x9J+k\ndBgYqiKpZK0Fad/qM4ivbgkMijXhGFODhWs/GlQWnPeaLusRnn3T/w2CsFzM kf0i\n6fFT3FAQBU5LCZs1Fp/XFRrnFMp+sNhbmdfnI9EDyZOXzlRS4O48k/AW/nSkCozk\nugYW+61H /RYPVEgF4VNxRqn+uA==\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n", "username": "gopro", "password": "Gzt2m6YMvLAo", "ip_address": "192.168.50.103" } Certificate written to C:\Users\user\gopro\OpenGoPro\demos\python\tutorial\tutorial_modules\tutorial_9_cohn\cohn.crt -
TODO
Communicating via COHN
Once the GoPro has provisioned for COHN, we can use the stored credentials for HTTPS communication.
For the setup of this demo, there is no pre-existing BLE or WiFi connection to the GoPro. We are only going to be using HTTPS over the provisioned home network for communication.
In order to demonstrate COHN communication we are going to Get the Camera State.
-
The code shown below is taken from
communicate_via_cohn.py. The credentials logged and stored from the previous demo must be passed in as command line arguments to this script. Runpython communicate_via_cohn.py --helpfor usage.We’re going to use the requests library to perform the HTTPS request. First let’s build the url using the
ip_addressCLI argument:url = f"https://{ip_address}" + "/gopro/camera/state"Then let’s build the basic auth token from the
usernameandpasswordCLI arguments:token = b64encode(f"{username}:{password}".encode("utf-8")).decode("ascii")Lastly we build and send the request using the above endpoint and token combined with the path to the certificate from the CLI
certificateargument:response = requests.get( url, timeout=10, headers={"Authorization": f"Basic {token}"}, verify=str(certificate), ) logger.info(f"Response: {json.dumps(response.json(), indent=4)}") -
TODO
This should result in logging the complete cameras state, truncated here for brevity:
Sending: https://192.168.50.103/gopro/camera/state
Command sent successfully
Response: {
"status": {
"1": 1,
"2": 4,
"3": 0,
"4": 255,
"6": 0,
"8": 0,
"9": 0,
...
"settings": {
"2": 1,
"3": 0,
"5": 0,
"6": 0,
"13": 0,
...
See the sending Wifi commands tutorial for more information on this and other HTTP(S) functionality.
Quiz time! 📚 ✏️
Troubleshooting
See the first tutorial’s troubleshooting section to troubleshoot any BLE problems.
See the Sending Wifi Command tutorial’s troubleshooting section to troubleshoot HTTP communication.
Good Job!
You have now provisioned COHN and performed an HTTPS operation. In the future, you can now communicate with the GoPro over your home network without needing a direct BLE or WiFi connection.
